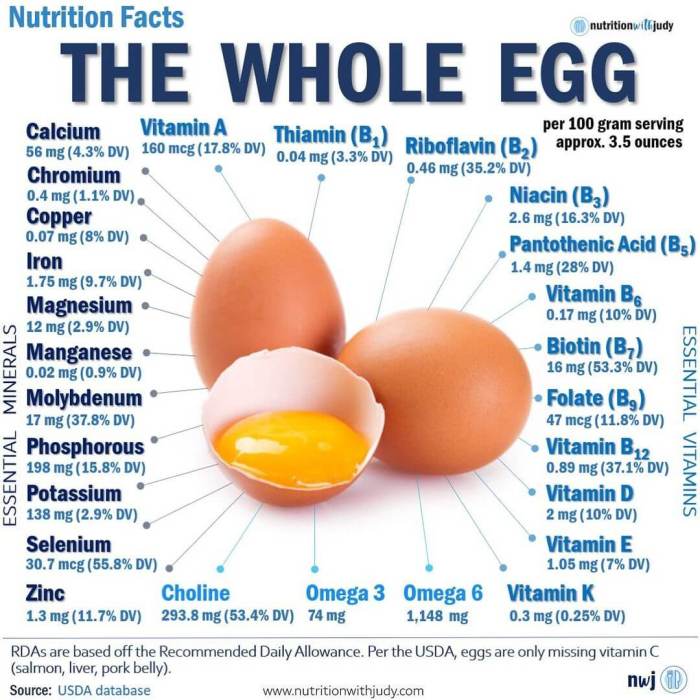
Egg Yolk Micronutrient Composition
Egg yolk nutrition facts – Egg yolks are nutritional powerhouses, far exceeding the nutritional profile of egg whites. They are a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals crucial for various bodily functions and overall health. Understanding the specific micronutrients present and their roles is key to appreciating the yolk’s significant contribution to a balanced diet.
Egg yolks contain a remarkable array of vitamins and minerals, each contributing to different aspects of health and well-being. The quantities vary slightly depending on factors such as hen breed, diet, and environmental conditions. However, the following list provides a general overview of the key micronutrients found in a single large egg yolk.
Vitamins and Minerals in Egg Yolks and Their Health Benefits
The following list details the vitamins and minerals found in egg yolks, along with their associated health benefits. It’s important to remember that these benefits are realized as part of a balanced diet and lifestyle, not solely from egg yolk consumption.
- Vitamin A (Retinol): A large egg yolk contains approximately 180 mcg of Vitamin A, crucial for vision, immune function, and cell growth. Deficiency can lead to night blindness and impaired immune response.
- Vitamin D: Providing around 40 IU, Vitamin D is vital for calcium absorption, bone health, and immune system regulation. Sunlight exposure also contributes to Vitamin D levels.
- Vitamin E (Tocopherols): With about 2 mg, Vitamin E acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals and supporting cardiovascular health.
- Vitamin K (Phylloquinone): A large egg yolk provides approximately 2 mcg of Vitamin K, essential for blood clotting and bone health. It plays a vital role in maintaining healthy blood vessels.
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): Around 0.6 mcg of Vitamin B12 is present, crucial for nerve function, red blood cell formation, and DNA synthesis. It’s particularly important for vegetarians and vegans.
- Choline: Egg yolks are an excellent source of choline, with approximately 140 mg per yolk. (Further details on choline’s role are provided below.)
- Iron: Contributing approximately 1 mg, iron is essential for oxygen transport in the blood and energy production. Iron deficiency can lead to anemia.
- Selenium: Egg yolks contain around 15 mcg of selenium, an antioxidant mineral that supports thyroid function and protects against cellular damage.
- Phosphorus: Providing approximately 100 mg, phosphorus is a key component of bones and teeth, and plays a role in energy metabolism.
The Role of Choline in Egg Yolks
Choline is a nutrient often overlooked, yet it plays a critical role in several bodily functions. Egg yolks are a particularly rich source of this essential nutrient. Its significance extends to brain health and liver function.
Choline is a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter crucial for memory, learning, and muscle control. Adequate choline intake is linked to improved cognitive function and reduced risk of age-related cognitive decline. Furthermore, choline aids in liver function by supporting the metabolism of fats and preventing fat buildup in the liver.
Vitamins and Minerals Important for Pregnant Women and Growing Children, Egg yolk nutrition facts
Several vitamins and minerals in egg yolks are particularly beneficial during pregnancy and childhood growth spurts. These nutrients support the development and healthy functioning of the developing fetus or child.
- Folate (Folic Acid): Although not explicitly listed above, it’s worth noting that while egg yolks contain some folate, it’s not a primary source. However, adequate folate is crucial for preventing neural tube defects in developing fetuses. Pregnant women should ensure they obtain sufficient folate from other dietary sources and/or supplements.
- Iron: The iron in egg yolks is vital for both pregnant women and growing children, supporting increased blood volume during pregnancy and red blood cell production in children.
- Choline: As mentioned earlier, choline is crucial for brain development in children and supports overall fetal development during pregnancy.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is essential for bone growth and development in children, and also plays a crucial role in calcium absorption during pregnancy.
Egg Yolk and Cholesterol: Egg Yolk Nutrition Facts
Egg yolks are a rich source of nutrients, but their cholesterol content has long been a subject of debate regarding their impact on human health. Understanding the relationship between egg yolk consumption and blood cholesterol levels is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will explore this relationship, examining research findings and clarifying the different types of cholesterol and their effects on the body.The relationship between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol is more nuanced than previously thought.
While it’s true that egg yolks contain cholesterol, the effect of consuming them on blood cholesterol levels varies significantly between individuals. Some people experience a minimal increase in blood cholesterol after eating egg yolks, while others show no significant change. This variation highlights the importance of individual responses and other dietary and lifestyle factors.
Impact of Egg Yolk Consumption on Cardiovascular Health
Numerous studies have investigated the link between egg yolk consumption and cardiovascular health. Some studies have shown a correlation between high egg consumption and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly in individuals already at high risk. However, other research suggests that moderate egg consumption (up to one egg per day) may not significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease for most healthy individuals.
Egg yolks are nutritional powerhouses, packed with vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats. It’s interesting to compare their nutrient profile to something like sugary drinks; for instance, checking out the coca cola nutrition facts highlights the stark contrast in nutritional value. Ultimately, understanding both helps us make informed choices about what we consume, emphasizing the importance of balanced nutrition.
These conflicting findings underscore the complexity of the issue and the importance of considering individual factors like genetics, overall diet, and physical activity levels. Many studies now focus on the overall dietary pattern rather than isolating single foods like egg yolks. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, even with moderate egg consumption, is generally associated with better cardiovascular health outcomes than a diet lacking these components.
Types of Cholesterol and Their Effects on the Body
Cholesterol exists in two main forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often called “good” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol contributes to the buildup of plaque in arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, helps remove cholesterol from arteries, protecting against heart disease.
In addition to these two types, there is also very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, which is a precursor to LDL cholesterol. The balance between these different types of cholesterol is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. While egg yolks contain cholesterol, their impact on the balance of these lipoproteins is complex and influenced by other dietary factors and individual metabolic processes.
Therefore, simply focusing on the cholesterol content of egg yolks without considering the broader dietary context can be misleading.
Egg Yolk in Different Diets
![]()
Egg yolks, while rich in nutrients, have varying roles and implications across different dietary approaches. Understanding their place within various eating plans is crucial for optimizing health and achieving dietary goals. This section will explore the integration of egg yolks into ketogenic, vegetarian, vegan, and paleo diets, considering both benefits and potential drawbacks.
Egg Yolk Inclusion in Various Diets
The following table summarizes the suitability of egg yolks within popular dietary plans. It’s important to remember that individual needs and dietary restrictions may necessitate modifications.
| Dietary Plan | Egg Yolk Inclusion | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ketogenic | Highly Suitable | High fat content supports ketosis; provides essential nutrients. | Cholesterol content should be monitored, especially for individuals with high cholesterol. |
| Vegetarian | Suitable | Excellent source of protein, fat, and micronutrients; complements plant-based sources. | May need to be balanced with other sources of nutrients, depending on the specific vegetarian approach. |
| Vegan | Not Applicable | N/A | Egg yolks are an animal product and therefore excluded from vegan diets. |
| Paleo | Highly Suitable | Whole food, naturally occurring; provides essential fats and nutrients. | Similar to ketogenic, cholesterol content should be monitored. |
Nutritional Comparison: Egg Yolks vs. Egg Whites
While egg whites are primarily a source of protein, egg yolks offer a significantly broader nutritional profile. This comparison highlights the key differences.
| Nutrient | Egg Yolk | Egg White |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Moderate | High |
| Fat | High | Negligible |
| Cholesterol | High | None |
| Vitamins (A, D, E, K) | High | Low or None |
| Minerals (Iron, Choline) | High | Low or None |
The significant difference lies in the fat-soluble vitamins and essential fatty acids found abundantly in the yolk, which are absent in the egg white. The yolk also contains choline, a crucial nutrient for brain health, which is lacking in the egg white. While egg whites provide a substantial amount of protein, the yolk’s rich nutrient profile makes it a more complete food source.
FAQ Explained
Are egg yolks good for your eyes?
Yes, egg yolks are a good source of lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that support eye health and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Can people with high cholesterol eat egg yolks?
The effect of egg yolk consumption on cholesterol levels varies among individuals. While some studies show minimal impact, it’s best to consult a doctor or registered dietitian for personalized advice, especially if you have existing high cholesterol.
Are egg yolks a good source of iron?
While egg yolks contain iron, the bioavailability (how well the body absorbs it) is relatively low compared to other iron sources like red meat. However, they still contribute to overall iron intake.
How many egg yolks should I eat per week?
Recommended weekly intake varies based on individual health status and dietary needs. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Are there any allergies related to egg yolks?
Yes, egg allergies are common, primarily affecting children. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and individuals with egg allergies should strictly avoid egg yolks.